bohr's atomic model-

postulates-
1.electrons revolve around nucleus in concentric circular path called orbit situated at definite distance from the nucleus.
2.as long as electron remains in particular orbit, it neither emits nor absorbs energy.
3.different stationary levels are represented as K,L,M,N.
4.Energy go on increasing as we go away from nucleus.
5.a definite amount of energy is absorbed when electron jump from lower energy level to higher energy level and electron jumps from higher energy level to lower energy level and releases energy which is equal to difference between that 2 energy levels .
6. an electron can move in that stationary orbit without radiating energy for which angular momentum(mvr) is equal to integral multiple of h/2pi
for K shell n=1 , for L shell n=2, for M shell n=3 , for N shell n=4.
Idea of shell , sub shell and orbital-
1. shell-
the orbit in which electron revolves is called as principal energy level or shell. the maximum no. electrons that revolves in particular orbit is equal to 2n^2.
2. sub shells-
a principal shell is further divided into sub shell.
3. orbital-
the 3-d region around nucleus in which probablity of finding electron is more is called orbital.
each sub shell is further divided into one or more energy states called as orbitals.
shapes of s and p orbitals-
s orbital-
s orbital is non directional.
it is spherically symmetrical around the nucleus.
the size and energy of s orbital increases with increase in principal energy level that is in order 4s>3s>2s>1s.
p orbital-
p orbital is dumb bell shaped ,having 2 lobes on either sides of the imaginary plane that passes through nucleus.
there are 3 orientations of the electron cloud in p orbital,along the 3 co-ordinate axes x,y and z.
the size and energy goes on increasing in order 4p>3p>2p>1p.
the size,shape and energy of 3 orbitals are identical.
Quantum numbers-
the numbers which are used to identify the various energy states of an electron is called quantum numbers.
following 4 are quantum numbers
1. principal quantum number(n)-
indicates the main or principal energy level of electron
determines the size of the electron cloud
it also gives information about maximum no of electrons can be acoomodated in a shell.
2. azimuthal / subsidiary / orbital quantum number (l)-
gives shape of orbital
gives subshell to which electron belogs
magnetic quantum number(m)-
indicates the spatial orientation of each sub shell i external magnetic field
positive value of m indicates orientation of orbital and magnetic field are in same direction. negative value of m indicates orientation of orbital and magnetic field are in opposite direction.
spin quantum number(s)-
it gives information about revolution of electron about its own axis.
+1/2 for clockwise and -1/2 for anticlockwise.
order of filling of atomic orbitals
anomalous behavior of Cu and Cr-
it is for attaining more stability in Cu and Cr by having completely filled or half filled orbitals.


Basic Idea-
A crystal is a substance which is formed by repetition of 3-d identical units,where a unit may contain one or more atoms.
Some crystallographic terms-
lattice-
is a periodic array of geometric points arranged in space such that each point is identical to surrounding.
Basis-
is obtained by placing an atom or group of atoms at each lattice point in regular manner.
lattice+basis=crystal.
unit cell-
this is the region of the crystal defined by basis vectors a,b,c.
lattice constant-
a,b,c , alpha , beta , gama are lattice constants.
Bravais lattice-
there are only fourteen ways of arrangements of points about given point
some basic structures-
cubic lattice-
there are 3 basic cubic lattice
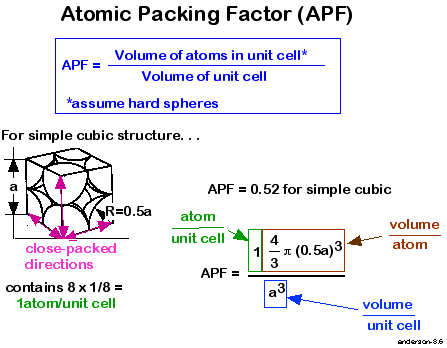
simple cubic- no of atoms=8*1/8=1example-polonium
body centered cubic=8*1/8+1=2 example-Ba,Fe,K,Li
face centered cubic=8*1/8+6*1/2=4 example-Al,Ca,Cu,Ni
packing fraction-
it is the ratio of volume of the sphere in unit cell to the volume of unit cell.
Miller indices-the orientation of a crystal plane within the crystal can be determined by any three nonlinear points in the plane.
if each of the points lies on crystal axis, the position and the orientation of the plane may be obtained by specifying the location on the axis in terms of lattice constants on basis vectors


thermodynamics-
if a number properties of the system eg. pressure, temperature, volume etc; are known, many phenomena can be studied even without a detailed knowledge of molecular movement of gas. in such cases we can apply some general laws related to energy, its changes and the quantities associated to it. the branch of physics which includes this is known as thermodynamics.
limitations-
1.it deals with matter on macroscopic scale i.e. system relatively large and involving many molecules. it does not give any information about individual atoms and molecules.
2.it does not consider the time factor and speed of transformation or change.
3.it is interested only in initial and final state and not in mechanism of process.
concept of thermodynamics-
system-
the portion of the universe under thermodynamic consideration is called system.
surroundings-
the remaining portion of the universe excluding system is called surroundings.
boundary-
the wall separating system and surroundings is called boundary.
types of systems-
open system-
when system can exchange both matter and energy.
example-
closed system-
when system can exchange only energy with surrounding not matter.
example-
isolated system-
when system can not exchange both energy and matter.
example-
3 types of systems in thermodynamics-
properties of system-
they are divided into 2 types
1.extensive property-
whose magnitude depends on amount of matter present in the system.
examples- mass, volume,heat,work,surface area,internal energy,enthalpy,heat capacity,pressure
2.intensive property-
whose magnitude does not depend upon amount of matter.
examples-surface tension,density,viscosity,refractive index,temperature,boiling point,melting point,specific heat
thermodynamic function or state function-
every system has thermodynamic properties such as temperature, pressure, volume.these variables are called as state variables.
change of state-
the system remains in given state as long as values of state variables remain constant. when one or more variables change,the system enters in new state.
state function-
any property of a system ,which depends upon only on current state of system and it is independent of path followed to reach that state .
properties of state function
1.if state function of a system is specified by fixing the values of some of the state functions ,the values of all other state functions are fixed.
example-if we specify the mass , temperature ,pressure of water its volume and energy are automatically fixed. therefore energy is also state function.
2.when state function undergoes change of state, the change of any state depends only upon initial and final states of system.
internal energy-
internally generated energy i.e. due to vibration,rotation,bonding of molecules, latent heat etc. it is a state function
thermodynamic equilibrium-
system is said to be in thermal equilibrium if there is no change in thermodynamic function with time.
for system to be in thermodynamic equilibrium , it has to attain following 3
types of equilibrium.
thermal equilibrium-
system and surrounding at same temperature. no exchange of heat between system and surrounding.
chemical equilibrium-
composition of system does not change with time
mechanical equilibrium-
no movement of matter from one part of system to other part with respect to surrounding.
system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium if
1.macroscopic properties vary with time.
2.no currents of matter and energy within the system or at its boundary
types of process-
isothermal process-
process in which temperature remains constant.
isobaric process-
process in which pressure remains constant.
isochoric process
process in which volume remains constant.
adiabatic process-
process in which internal energy remains constant.
cyclic process- system returns to initial point after completing of process.
reversible process-
if system goes to one pt to other pt by one path and retraces same path to reach initial point.
irreversible process-
a process which proceeds in definite direction and can not reversed at any stage
heat-
it is a form of energy. when heat is supplied to system, then temperature of system increases. temperature of system falls as heat is removed from system. heat is chaotic form of energy and it can not be completely converted into work. it is not a state function.
work-
it is one of the modes of transfer energy with surroundings. it is product of force and displacement.
law of conservation of mass and energy-
the sum of mass and energy in the universe is constant.
enthalpy of system(H)-
it is the total internal energy and p-v type energy of the system.




.jpg)